Ever wondered what those mysterious wires, switches, and boxes lurking behind your walls are all about? Delving into the world of electrical house wiring parts can feel like entering a secret language, but it’s actually a fascinating system that brings power and comfort to our homes. This guide serves as your roadmap, explaining the names and functions of key components, all organized for easy reference in a downloadable PDF format.
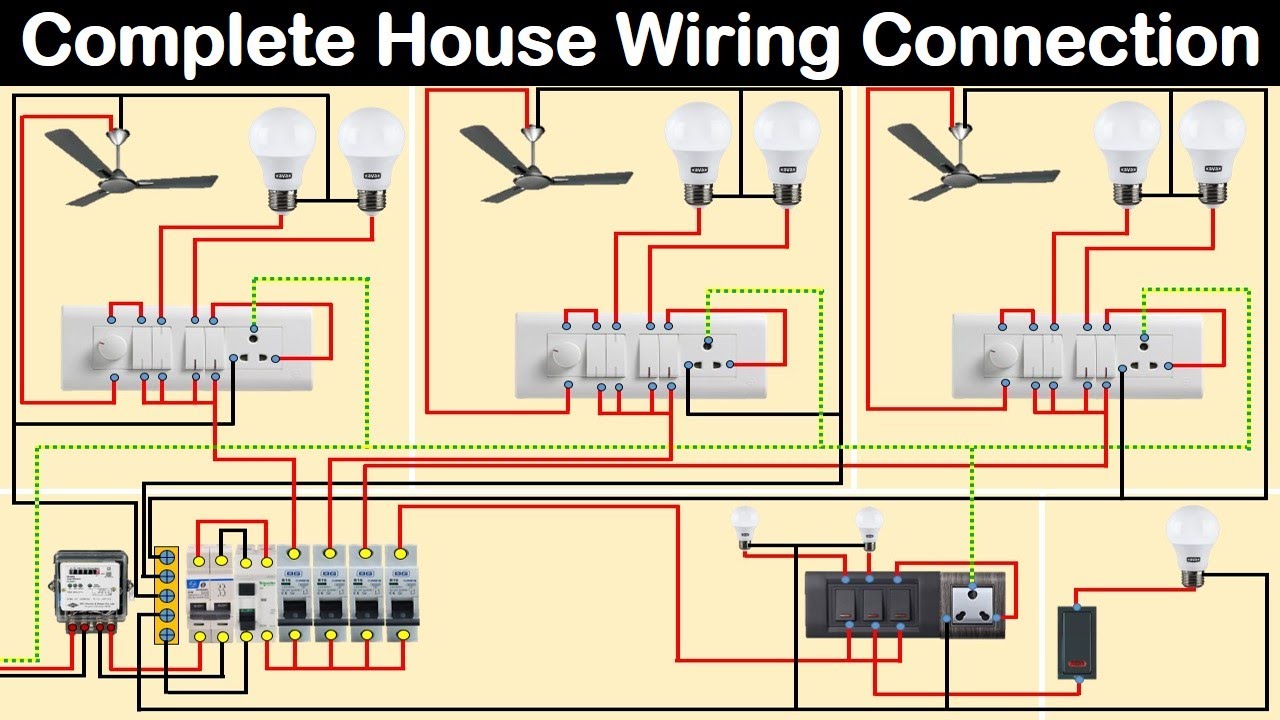
Image: guidediagramluann.z21.web.core.windows.net
Understanding electrical wiring is not just a matter of curiosity; it’s a handy skill to have when tackling repairs, home improvement projects, or simply navigating the jargon of your next electrical upgrade. Our PDF provides a clear breakdown of the parts involved, making it easier to discuss these elements with electricians, troubleshoot common issues, and even gain a deeper appreciation for the safety measures that protect your home.
Unveiling the Basics: Electrical Wiring Components and their Roles
Think of your home’s electrical system as a network of roads carrying electrical power to various destinations—your lights, appliances, and outlets. These roads are made up of wires, conduits, and numerous other components that work together seamlessly. To understand the system’s intricate workings, let’s delve into the names and functionalities of the key players.
Wires: The Backbone of Electrical Circuits
Wires are the veins that carry electrical current throughout your home. They come in different sizes and types, each suited for specific applications.
- Hot Wire (Black): This wire carries the energized current from the power source.
- Neutral Wire (White): This wire completes the circuit, providing a path for the current to return to the source.
- Ground Wire (Green or Bare Copper): This critical wire safeguards you by offering a path for stray current to flow to the ground, preventing electric shocks.
Conduit: Protecting the Wires
Conduit, a protective tubing, shields the wires from damage, moisture, and fire hazards. It comes in various materials like PVC (polyvinyl chloride), metal, and flexible options.
- Electrical Boxes: These enclosures hold junction points in the wiring system, providing a secure and organized space for connecting wires.
- Junction Boxes: These boxes serve as connection points for wires, allowing for easy modification and repair.
- Outlet Boxes: These boxes hold electrical outlets, providing a safe and accessible point for plugging in devices.
- Switch Boxes: These boxes accommodate switches that control electrical circuits.
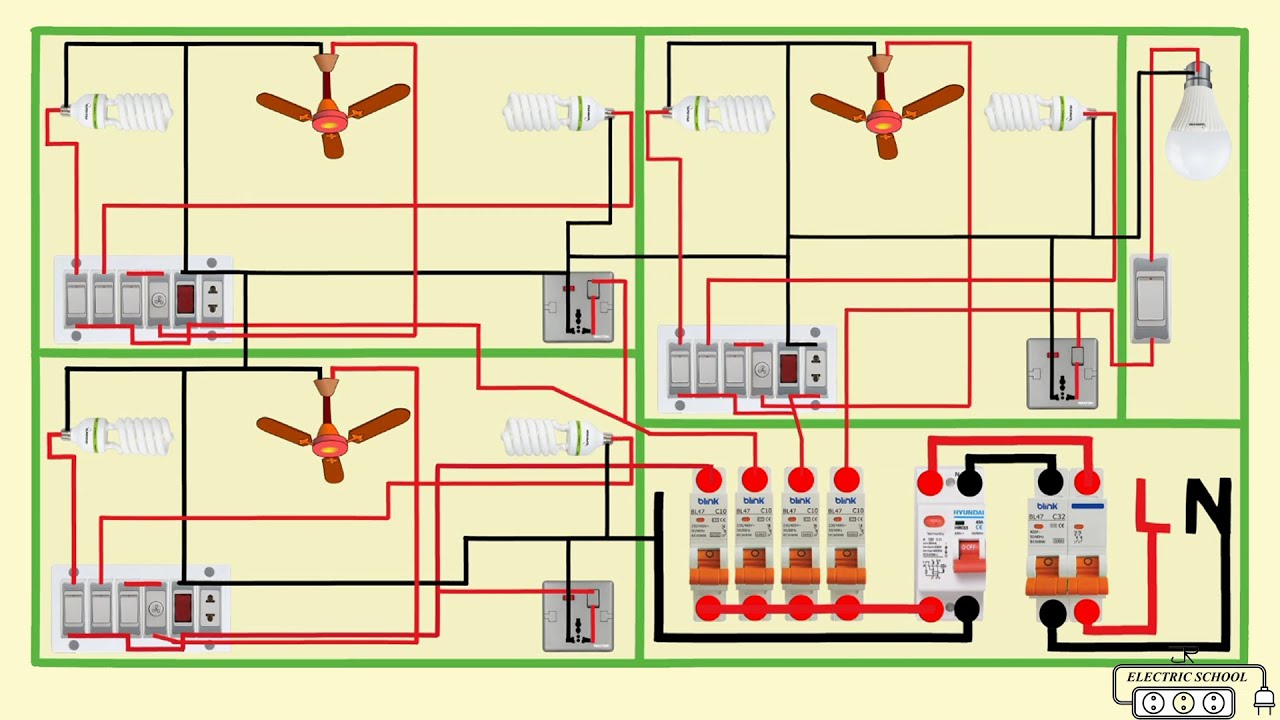
Image: userlibrarybernard.z13.web.core.windows.net
Switches: Controlling the Flow of Electricity
Switches act as gatekeepers, allowing you to turn electrical devices on and off.
- Single Pole Switches: These switches control a light or appliance from one location.
- Double Pole Switches: These switches control a light or appliance from two different locations.
- Three-Way Switches: These sets of switch pairs (typically two) control a light or appliance from three different locations.
Outlets: Feeding Your Devices
Outlets provide convenient access points for plugging in our electronics.
- Receptacles (Outlets): These electrical outlets come in various configurations to accommodate different types of plugs.
- GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) Outlets: These outlets provide an extra layer of safety in areas prone to moisture, like bathrooms and kitchens.
- AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter) Outlets: These outlets offer protection against electrical arcing, which can be a fire hazard.
Breaker Panels: The Central Control Center
The breaker panel, the heart of your home’s electrical system, houses circuit breakers. These devices safeguard your wiring and appliances by automatically interrupting the flow of electricity in case of a fault or overload.
- Circuit Breakers: These devices are designed to break the circuit, preventing damage to wiring and appliances in case of overload.
- Main Breaker: This breaker controls the entire electrical system and can shut off the power supply to your home.
Imagine a world without the ability to turn on a light, power a refrigerator, or charge your phone. Electrical wiring, though often hidden from view, is the essential foundation that connects our daily routines with the power that makes it all possible. It’s a system that demands respect and understanding, and by learning about its components, you gain a valuable awareness of how this vital infrastructure keeps your life running smoothly.
A Deeper Dive: Understanding the Technical Aspects
Now that we’ve explored the basic components, let’s delve into some of the technical aspects of wiring that will help you decipher the language of electricians and navigate DIY projects with greater confidence.
Current, Voltage, and Resistance: The Language of Electricity
Electrical circuits operate based on the interplay of three key elements:
- Current (Measured in Amps): The flow of electrical charge through a circuit, similar to the flow of water through a pipe.
- Voltage (Measured in Volts): The electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit; it’s the force that pushes the current through the circuit.
- Resistance (Measured in Ohms): The opposition to the flow of current in a circuit. It’s like friction in a pipe, slowing down the flow of water.
Circuit Types: Understanding the Flow of Electricity
Electrical wiring utilizes different types of circuits to deliver power effectively:
- Series Circuit: In this circuit, devices are connected in a single line, so if one device fails, the entire circuit breaks down. Think of Christmas lights wired in series; if one bulb breaks, the entire string goes dark.
- Parallel Circuit: In this circuit, devices are connected independently to the power source. If one device fails, the other devices remain unaffected. Think of the outlets in your home, where a single outlet can be used without disrupting other outlets.
Voltage Ratings and Amperage: The Power behind Your Circuits
The components of your electrical system are rated for specific voltage and amperage to ensure safe and efficient operation.
- Voltage Rating: Indicates the voltage a component is designed to handle.
- Amperage Rating: Indicates the maximum current a component can handle safely.
Wiring Gauge: Sizing the Wires for Safety and Efficiency
The thickness of a wire, known as its gauge, dictates how much current it can carry safely. The lower the gauge number, the thicker the wire and the higher its current carrying capacity.
- Ampacity: The maximum current a wire can safely carry, determined by the wire’s gauge and the temperature of its surroundings.
- Choosing the Right Gauge: Select the appropriate wire gauge based on the amperage requirements of the circuit and the length of the run.
Safety Regulations: Protecting Your Home
Electrical wiring is a complex system, and it’s crucial to adhere to safety regulations and best practices.
- National Electrical Code (NEC): This code sets safety standards for electrical installations in residential and commercial buildings.
- Qualified Electrician: Always hire a qualified electrician for any electrical work; they are familiar with the NEC and can ensure safe installation and repairs.
Exploring Resources for Home Electrical Knowledge
While this article provides a comprehensive overview of electrical house wiring parts, there are numerous resources available to delve deeper into the world of residential electrical systems.
- Online Guides and Tutorials: Websites like HomeAdvisor, Family Handyman, and This Old House offer articles, videos, and step-by-step guides on various aspects of electrical wiring.
The Importance of Continuous Learning
Electrical wiring is an ever-evolving field. New technologies, safety standards, and product innovations are constantly emerging. Continuous learning is essential for staying informed and ensuring your electrical system remains safe, efficient, and up-to-date.
Electrical House Wiring Parts Name Pdf
Conclusion: Empowering Yourself with Electrical Wiring Knowledge
This guide has equipped you with a foundational understanding of electrical house wiring parts, empowering you to engage in conversations with professionals, tackle simple repairs, and appreciate the intricate systems that bring power to your home. Download the attached PDF for a handy reference guide that you can keep close at hand. And remember, while DIY electrical projects might seem tempting, safety should always come first. Consult a qualified electrician for any complex electrical work or installations to ensure the integrity of your electrical system and the safety of your home.






