Imagine a tiny, invisible particle speeding across the vast universe. It’s moving at a constant pace, neither slowing down nor speeding up. This seemingly simple concept is the heart of the “constant velocity particle model,” a foundational principle in physics that helps us understand how objects move.

Image: www.coursehero.com
This article delves into the fascinating world of this model, focusing on Worksheet 3, a crucial step in mastering this fundamental concept. We’ll explore the key problems, their solutions, and the insights they offer into the mechanics of movement.
Stepping into the Realm of Uniform Motion: Mastering the Constant Velocity Particle Model
The constant velocity particle model is a simplified representation of motion where an object is treated as a point mass moving at a constant speed in a specific direction. This means the object’s velocity remains unchanged over time, leading to a predictable and straight-line trajectory.
Worksheet 3 serves as a stepping stone in understanding the application and nuances of this model. It presents a series of problems that challenge students to apply the concepts of constant velocity, displacement, time, and distance. By solving these problems, students can develop a deeper understanding of the relationships between these variables and how they dictate the motion of an object.
Navigating the Nuances of Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3
Worksheet 3 typically delves into different facets of the constant velocity model, focusing on real-world scenarios. Let’s break down some common types of problems and approaches to solving them:
1. Calculating Distance:
- Problem: A car travels at a constant velocity of 60 miles per hour for 3 hours. What distance does it cover?
- Understanding the Formula: Distance = Velocity x Time
- Solution: Distance = 60 miles/hour x 3 hours = 180 miles
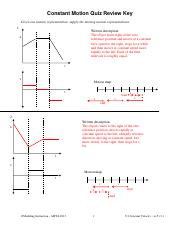
Image: www.coursehero.com
2. Determining Time:
- Problem: An airplane flies at a constant velocity of 500 kilometers per hour. How long does it take to travel a distance of 2500 kilometers?
- Understanding the Formula: Time = Distance / Velocity
- Solution: Time = 2500 kilometers / 500 kilometers/hour = 5 hours
3. Calculating Velocity:
- Problem: A cyclist completes a 10-kilometer race in 30 minutes. What is their average velocity?
- Understanding the Formula: Velocity = Distance / Time
- Solution: Velocity = 10 kilometers / 0.5 hours = 20 kilometers/hour (Note: We convert 30 minutes to 0.5 hours for consistency in units).
4. Analyzing Graphs:
- Problem: A graph shows the position of a moving object over time. How can you determine if the object is moving at constant velocity based on the graph?
- Understanding the Concept: A straight line on a position-time graph indicates constant velocity.
- Solution: If the line is slanted, it means the object is moving at a constant velocity. The steeper the slope, the faster the velocity. A horizontal line indicates the object is at rest (zero velocity).
Beyond the Worksheet: Real-World Applications of the Constant Velocity Model
The constant velocity model might seem like a simplified approach, but its applications are far-reaching.
- Navigation: Navigating ships and airplanes relies on calculating distances, speeds, and travel times, all based on principles of constant velocity.
- Traffic Flow: Traffic engineers use the model to analyze traffic flow patterns and optimize traffic light timings.
- Robotics: Robots programmed to move in straight lines use the constant velocity model to perform repetitive and precise tasks.
- Space Exploration: Predicting the trajectories of spacecraft in space involves the application of the constant velocity model, albeit with added factors such as gravity.
Expert Insights and Actionable Tips for Mastering the Constant Velocity Model
Here are some valuable insights from experienced physics instructors to make your journey through this concept smoother:
- Visualize: Draw diagrams and visualize the scenarios to gain a better understanding of the relationships between velocity, distance, and time.
- Break Down Problems: Decompose complex problems into smaller, more manageable steps.
- Practice Regularly: Consistent practice with different types of problems will solidify your understanding.
Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3 Answer Key
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Simplicity
The constant velocity particle model, though simplified, offers a powerful tool for understanding the fundamental principles of motion. By embracing the underlying concepts and applying them through practice, you can unlock a deeper appreciation for the laws that govern our world.
This journey to understanding the constant velocity model, especially through Worksheet 3, is not just about solving problems; it’s about developing the skills to analyze, predict, and interpret the motion of objects. So, keep observing, keep learning, and keep your eyes on the path of motion!






